Fetal Trisomes and Syndromes
· Triploidy- Severe IUGR abnormal head shape, cleft lip/palate, neural tube defects, CHD (ASD and VSD), hydrocephalus, holoprosencephaly, cystic renal dysplasia, club foot and large cystic placenta. The vast majority of fetuses with this phenotype abort spontaneously, usually in the first trimester. Twenty percent of all chromosomally abnormal abortuses are thought to be triploid.
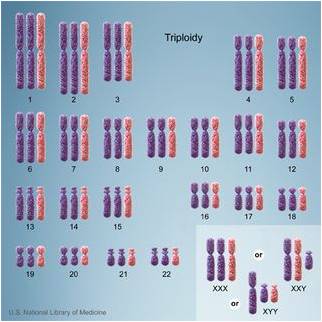 Triploidy
Triploidy
· Trisomy 21- (Down’s syndrome) The most frequently occurring trisomy in liveborn. Sonographic features include: thickened nuchal skin fold (>3 mm in fetus 12—15 weeks, >6 mm after 20 weeks), TOF CHD (ASD, VSD, tetralogy of Fallot), duodenal atresia, hydrops fetalis, isolated pleural effusion/ascites, and hypoplasia of the middle phalanx of the fifth finger (phalanges visible 15 — 16 weeks). Femoral lengths tend to be shorter than expected in relation to BPD. Currently less than 10% are detected antenatally. This may improve with careful screening, particularly cardiac.
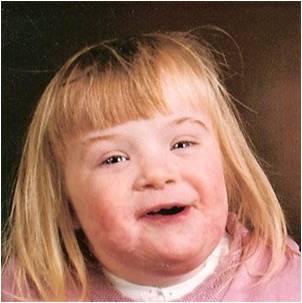 Trisomy 21
Trisomy 21
· Trisomy 18- (Edwards’ syndrome) Second most common chromosomal anomaly. This is a lethal condition, most fetuses being lost perinatally. Sonographic features include IUGR, prominent occiput, PH or OH, micrognathia, low set malformed ears, hydrocephalus, choroid plexus cysts, short sternum, CHD (VSD, Fallot’s tetralogy), diaphragmatic hernia, omphalocele, renal anomalies, tracheoesophageal fistulas, hands held in abnormal position, talipes.
· Trisomy 13- (Patau's or Bartholin-Patau syndrome) Microphthalmia cleft lip/palate, polydactyly, digits held in fixed flexion, holoprosencephaly, omphalocele, CHD(90%), ACC, micrognathia hypotelorism, malformed ears, hydronephrosis and polycysric kidneys. The condition is lethal.
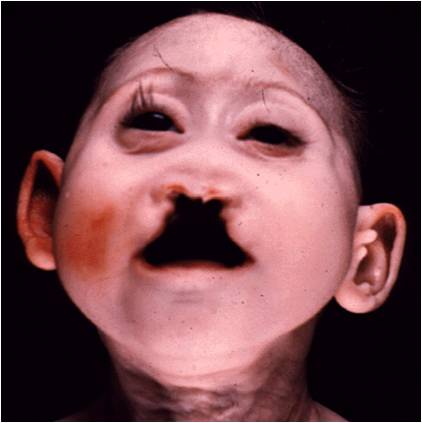 Trisomy 13
Trisomy 13
· Turner's syndrome- Sonograpgic features include cystic hygroma and hydrops, horse shoe kidney, skeletal abnormalities, including radial aplasia. Cystic hygromas often regress.
 Turner's syndrome
Turner's syndrome
· Trisomy 9- IUGR, craniofacial anomalies, misshaped ears, narrow chest, kyphoscoliosis, CHD, renal malformations, cystic dilatation of the fourth ventricle with lack of midline fusion. Prognosis is extremely poor.
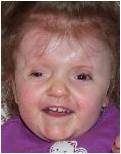 Trisomy 9
Trisomy 9
· Trisomy 20- Craniofacial anomalies, hypo- or hypertelprosm, large poorly formed ears, limb anomalies, vertebral defects, kyphoscoliosis, hydrocephalus, umbilical hernias, CHD and renal malformations. Prognosis depends upon associated malformations.
· Trisomy 9p- Hypertelorism, prominent nose, cleft lip/palate, kyphoscoliosis and CHD; 10% die in early childhood, survivors have variable mental and other handicaps.
· Trisomy 12- Midface hypoplasia, small ears, turribrachycephaly with a high forehead, cleft palate, CHD and clindactyly of the 5th finger. Sonography is non-specific but when any combination of the above anomalies are seen, amniocentesis and chromosomal analysis is indicated.
· Trisomy 10- IUGR, microcephaly, microphthalmia, cleft palate, malformed ears, camptodactyly, syndactyly, CHD, kyphoscoliosis, vertebral anomalies, brain and ocular malformations and gut malrotation; 50% die from CHD. Survivors are mentally retarded.
· Trisomy 8- Prominent forehead, hypertelorism, camptodactyly of fingers and toes, hydrocephalus, CHD and urogenital anomalies; 10% die in the first 2 years. Mental retardation is mild to moderate.
 Trisomy 8
Trisomy 8
· Trisomy 10- IUGR, dolichocephaly, dysokactic ears, cleft lip/palate, club foot, CHD and renal cystic disease. Half of the fetuses are stillborn or die in the postnatal period. Survivors show mental and motor deficiency.
Back to Structural Fetal Abnormalities